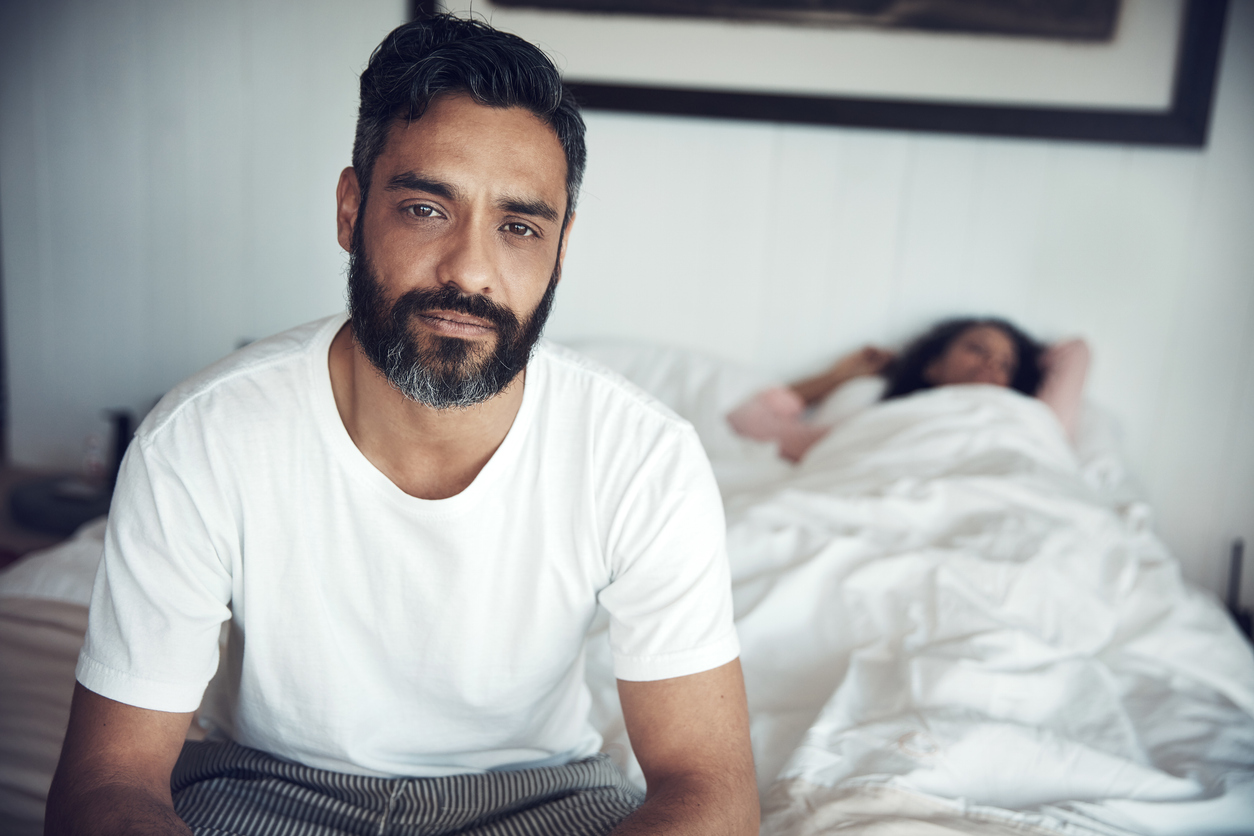
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also known as impotence, is a widespread condition affecting a significant number of men globally and in the UK. It’s defined as the recurring inability to achieve or maintain a sufficiently firm erection for sexual intercourse. While it’s a sensitive topic, understanding the risk factors and potential remedies can help men manage this condition.
What is Erectile Dysfunction (ED)?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a condition that prevents a man from achieving or maintaining a firm erection for sexual intercourse. An erection occurs when blood flows into the penis, expanding its tissues. This process is influenced by both physical and psychological factors. During arousal, nerves send signals that relax the muscles surrounding the blood vessels in the penis, allowing increased blood flow and creating an erection.
What are the Risk Factors for Erectile Dysfunction?
ED is a condition that affects many men and can significantly impact their quality of life. Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be influenced by various risk factors, including:
Risk Factor 1: Physical Effects of Erectile Dysfunction
The primary physical consequence of erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to achieve or maintain a firm erection. This can result in:
- Reduced sexual satisfaction: ED can significantly diminish a man’s enjoyment and fulfilment during sexual activity.
- Strained relationships: Difficulty with sexual performance can create distance, frustration, and challenges within a relationship.
- Painful intercourse: In some cases, ED may be caused by underlying conditions affecting blood flow or nerves in the penis, leading to discomfort or pain during erections.
Risk Factor 2: Underlying Health Conditions
While ED is not a disease itself, it often signals an underlying health issue. Identifying these physical causes is essential for effective treatment. Some common factors include:
- Vascular problems: Adequate blood flow is crucial for achieving an erection. Conditions like atherosclerosis (hardened arteries) and high blood pressure can restrict blood flow to the penis, making it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection.
- Neurological issues: Nerve damage resulting from conditions such as diabetes or spinal cord injuries can disrupt the signals necessary for an erection.
- Hormonal imbalances: Low testosterone levels can contribute to ED.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity can all negatively impact erectile function.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves and blood vessels, leading to ED.
Risk Factor 3: Psychological Effects of Erectile Dysfunction
Studies indicate that approximately 5 million men in the UK experience some form of ED. The prevalence increases with age, affecting around 1 in 4 men over 40. Certain lifestyle factors also elevate the risk of ED, including:
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and restricts blood flow, impacting erectile function.
- Obesity: Excess weight can contribute to vascular problems and hormonal imbalances, both of which can lead to ED.
- Alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can impair nerve function and blood flow, affecting erections.
- Stress: Chronic stress can elevate cortisol levels, a hormone that can negatively impact sexual function.
What is the Treatment for ED?
Fortunately, erectile dysfunction (ED) is a treatable condition. With medical advancements, various options are available:
- Oral medications: Medications like sildenafil (Viagra) or tadalafil (Cialis) are commonly prescribed to enhance blood flow to the penis and facilitate erections.
Curious about the best ED medication in the UK for your needs?
Don’t miss our informative blog post!
- Lifestyle modifications: Addressing underlying risk factors such as smoking, obesity, and stress can significantly improve erectile function.
- Vacuum pumps: These devices draw blood into the penis to create and maintain an erection.
- Suppositories or implants: In some cases, medicated suppositories or penile implants may be recommended for men who don’t respond well to other treatments.
- Counselling: Therapy can help address any psychological factors contributing to ED. For men experiencing stress, anxiety, or depression that’s affecting their erectile function, psychosexual counselling can be particularly beneficial.
Is there Home Remedy for Erectile Dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition, and many men wonder if there are natural or home remedies to address it. While these remedies may provide some relief for certain individuals, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Here are some home remedies for ED:
Lifestyle Modifications
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and improve blood flow.
Discover a sustainable approach to healthy weight loss. Read our blog
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps improve blood circulation, which is essential for erectile function. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Weight Management: Excess weight can contribute to ED. Losing weight can improve blood flow and overall health.
- Limit Alcohol and Tobacco: Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking can damage blood vessels and impair erectile function.
- Stress Management: Stress can negatively impact sexual function. Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing.
Natural Supplements
- Ginseng: Some studies suggest that ginseng may improve erectile function in men.
- L-arginine: This amino acid is a precursor to nitric oxide, a substance that helps relax blood vessels and improve blood flow.
- Yohimbe: This herbal supplement may help increase blood flow to the penis, but it can have side effects and should be used with caution.
Important Note: It’s crucial to note that while these home remedies can be helpful, they may not work for everyone. The underlying cause of ED can vary, and individual responses may differ. If you’re experiencing ED, it’s advisable to seek professional medical advice.
Key Takeaway
Remember: ED is a treatable condition. If you’re facing frequent difficulties with erections, it’s important to talk to your clinician. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve your sexual health, prevent potential health complications, and boost your overall quality of life. Don’t hesitate to seek help from a healthcare professional.
References
Erectile dysfunction (ED): Symptoms, causes, and treatment (2014) Healthline. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/erectile-dysfunction.
Erectile dysfunction: Symptoms & types (no date) WebMD. Available at: https://www.webmd.com/erectile-dysfunction/guide-chapter-erectile-dysfunction-symptoms-risks.
Erectile dysfunction (2023) The Urology Foundation. Available at: https://www.theurologyfoundation.org/urology-health/male-reproductive-organs-conditions/erectile-dysfunction/
Erection problems explained (2023) Viagraconnect.co.uk. Available at: https://www.viagraconnect.co.uk/en-gb/erection-problems/erection-problems-explained.
Ellis, M. E. and Jewell, T. (2020) Korean red ginseng for erectile dysfunction, Healthline. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/erectile-dysfunction/korean-red-ginseng (Accessed: August 23, 2024).
L-ARGININE: Overview, uses, side effects, precautions, interactions, dosing and reviews (2020) Webmd.com. Available at: https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-875/l-arginine
Pearson, K. and RD (2023) Yohimbe: Benefits, uses and side effects, Healthline. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/yohimbe