Ah Weight Loss!
Many of us dream of a trimmer physique, but excess weight can be a stubborn foe.
Despite a healthy diet and exercise, some individuals find weight loss incredibly challenging. Often, uncontrollable hunger stands in their way. This is where weight-loss medications, prescribed by healthcare professionals alongside a calorie-restricted diet, can play a crucial role.
With so much conflicting information out there, making weight-loss decisions can be overwhelming. But you’ve taken a great first step by considering medications.
Now, the question remains: Weight loss injections or weight loss tablets? Both offer a potential path to weight loss, but which one is right for you?
This blog will delve into the UK’s most popular weight-loss medications, exploring their effectiveness, safety, and how they can support your weight-loss journey.
Weight Loss Medication: What You Need to Know
Weight loss medications can be an effective tool to support weight management.
These medications achieve weight loss through various mechanisms, including:
- Appetite suppression: Certain medications curb hunger cues, leading to reduced food intake.
- Decreased fat absorption: Some medications inhibit the intestinal absorption of dietary fat.
- Enhanced metabolic rate: A select few medications may increase the body’s basal metabolic rate, promoting calorie expenditure.
Clinical trials have demonstrated that prescription weight loss medications can achieve a modest yet statistically significant weight reduction, typically ranging from 5-20% of body weight. However, interindividual variability exists, and the specific medication prescribed will influence the degree of weight loss achieved.
It is crucial to emphasize that these medications are intended to complement, not replace, dietary modifications and lifestyle changes, such as regular physical activity. A multi-modal approach that combines pharmacological therapy with behavioral interventions has been shown to optimize weight loss outcomes and improve the sustainability of weight management in the long term. This comprehensive approach is essential to mitigate weight regain, which is a frequent consequence following medication discontinuation.
Weight Loss Medications: Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Enhanced Weight Loss: When used in conjunction with dietary changes and regular physical activity, weight loss medications have demonstrated efficacy in promoting weight reduction.
- MHRA Approval: The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) is responsible for ensuring the safety, quality, and efficacy of medicines in the UK.
- NICE Recommendations: The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) provides guidance to the National Health Service (NHS) on the use of various weight loss medications and treatments.
- Potential for Improved Metabolic Health: Certain weight loss medications may offer additional health benefits by improving blood sugar control, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels.
- Telehealth Accessibility: For patients, access to weight loss medications can be facilitated through telehealth platforms, expanding treatment options.
Cons
- Individualized Suitability: Weight loss medications are not a one-size-fits-all solution and may not be appropriate for everyone. A thorough medical assessment is crucial to determine candidacy.
- Cost Considerations: The cost of weight loss medications can vary and this is depending on insurance coverage and may pose financial constraints for some patients.
- Potential for Side Effects: Like all medications, weight loss medications can cause side effects, some of which may be serious. Careful monitoring and open communication with a healthcare provider are essential.
- Weight Regain Risk: Discontinuing weight loss medications can lead to weight regain. Sustainable lifestyle modifications are crucial for long-term success.
- Evolving Research: Long-term safety data on some newer weight loss medications is still being established. Ongoing research is necessary to fully understand the long-term health implications.
Medications for Weight Loss in UK
In the UK, several medications are licensed by the MHRA for chronic weight management in patients meeting specific criteria. These medications are prescribed by a healthcare professional and used alongside lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications and regular physical activity, to promote weight loss and improve health outcomes.
Here are the main licensed weight loss medications in the UK:
Weight Loss Tablets:
- Orlistat: This is the generic form of the medication and can be prescribed by a doctor in various dosages depending on individual needs.
- Xenical: This is a brand name medication containing 120mg of orlistat per capsule. It’s available by prescription only.
- Alli: This is an over-the-counter brand containing a lower dose of orlistat (60mg per capsule) compared to Xenical.

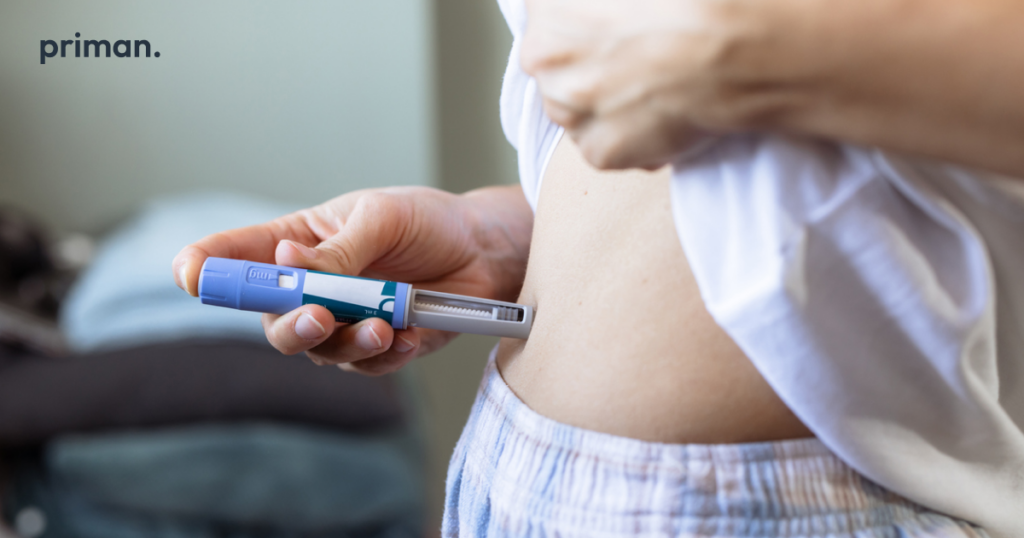
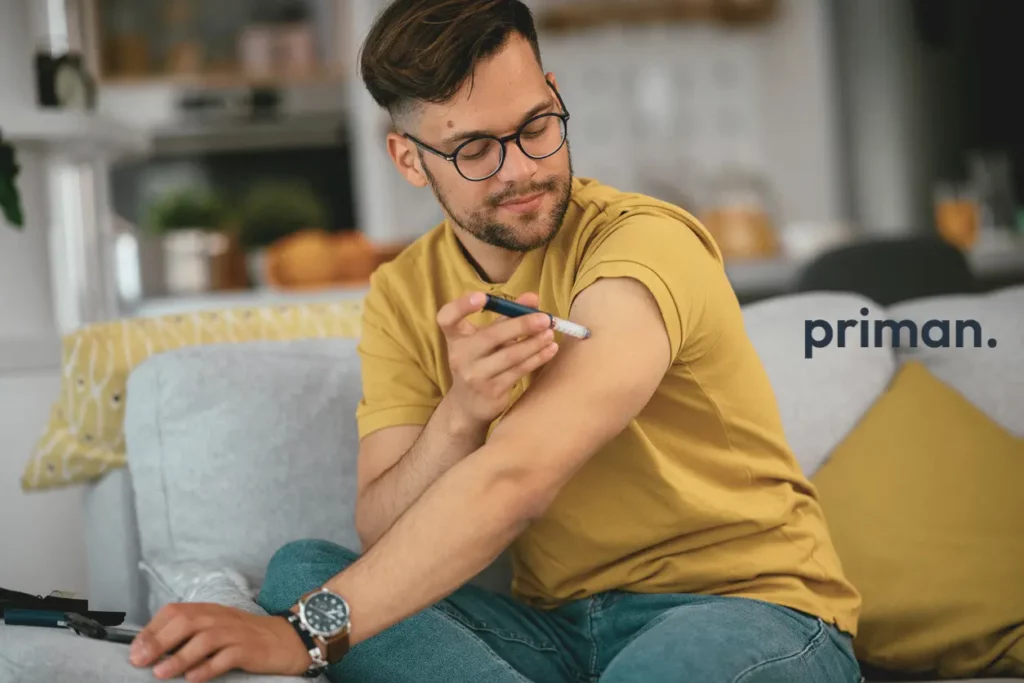
Weight Loss Injections:
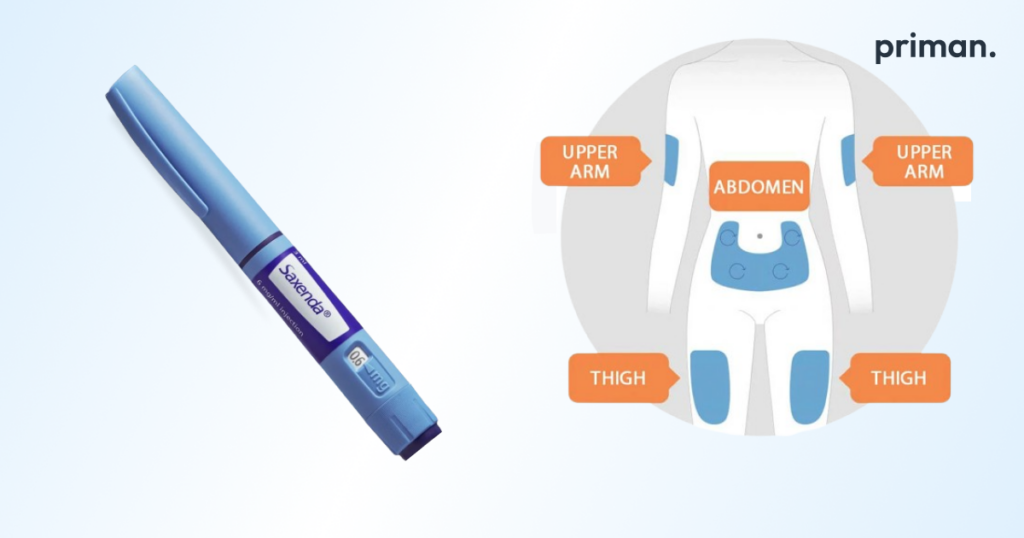
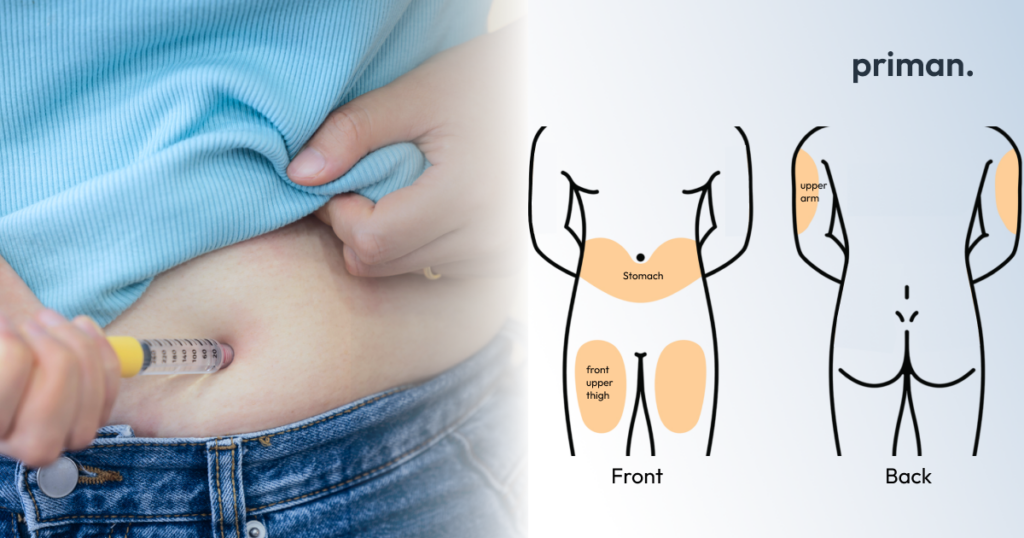
- Liraglutide (Saxenda): A daily self-administered injection that helps regulate appetite and blood sugar levels.
Additional info:
It is important to note that Ozempic (semaglutide) and Rybelsus (semaglutide) are currently not licensed for weight management in the UK. Their primary indication is for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, as evidenced by guidance from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE).
While not a licensed use, some patients taking these medications for type 2 diabetes may experience weight loss as a secondary effect. This is likely due to the medication’s impact on satiety and blood sugar control, as highlighted in research published in the National Institutes of Health (NIH) database.
Prior to the launch of Wegovy, which is specifically licensed for weight management, Ozempic may have been used off-label for this purpose in some cases. Off-label use should only be considered under the guidance of a healthcare professional, with a full understanding of the potential benefits and risks involved, as outlined in the guideline.
Selecting the right weight loss medication
The choice of weight loss medication is a personalised decision based on several factors. These include:
- Your Medical History: Certain medications may not be suitable for individuals with specific pre-existing health conditions.
- Body Mass Index (BMI): Different medications may be more effective for varying BMI ranges.
- Preference: Some medications are available as tablets, while others are administered via injection.
This table below provides an overview (with no specific order) of weight loss medications licensed in the UK that were discussed above. It’s important to remember that this information is for educational purposes only and should not be a substitute for professional medical advice.
| Medication | Type | Active Ingredient | Dosing schedule: | Effect on Body |
| Mysimba | Tablet | naltrexone and bupropion | Twice daily | Reduces Appetite |
| Orlistat | Tablet | Orlistat | 3 times daily, with each meal | Prevents fat absorption |
| Xenical | Tablet | Orlistat | 3 times daily, with each meal | Prevents fat absorption |
| Alli | Tablet | Orlistat | 3 times daily, with each meal | Prevents fat absorption |
| Saxenda | Injection | Liraglutide | Daily | Reduces Appetite |
| Wegovy | Injection | Semaglutide | Weekly | Reduces Appetite |
| Mounjaro | Injection | Tirzepatide | Weekly | Reduces Appetite |
If you’re considering weight loss medication, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. They can assess your individual needs, discuss potential medication options, and create a personalized weight management plan that may include lifestyle modifications and medication use, if appropriate.
Start your weight loss journey at Priman…Take part in the quick assessment.
Eligibility for Weight Loss Medications
Prescription weight loss medications are typically considered for patients meeting specific criteria. Here’s a general overview:
- Body Mass Index (BMI): Generally, a BMI of 30 or higher is considered a primary criterion for eligibility. In some cases, a BMI between 27 and 30 might be considered if accompanied by weight-related medical conditions or risk factors, such as type 2 diabetes or hypertension.
- Age: Patients must typically be 18 years or older.
- Individual Medical Assessment: A thorough medical history evaluation is necessary to determine a patient’s suitability for these medications. This assessment considers factors such as pre-existing conditions and potential interactions with current medications.
Medication-Specific Criteria
It’s important to note that each weight loss medication may have its own additional prescribing criteria established by regulatory bodies.
Evidence from Clinical Trials
Prescription weight loss medications can be a valuable tool to support weight management efforts when used alongside lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications and regular physical activity. These medications have undergone clinical trials to assess their safety and efficacy in promoting weight loss.
Each licensed weight loss medication in the UK has undergone rigorous evaluation by the MHRA to demonstrate its effectiveness in promoting weight loss. However, the specific mechanism of action and optimal application may vary between medications.
| Medication | Clinical Trials |
| Mysimba | Lost up to an average of 8.1% of their starting weight after 56 weeks of treatment |
| Orlistat | 37% of people lose up to 5% or more of their starting weight after 12 weeks |
| Xenical | 37% of people lose up to 5% or more of their starting weight after 12 weeks |
| Alli | 46.7% of people lose up to 5% or more of their starting weight after 6 months |
| Saxenda | Lost up to an average of 6.3% of their starting weight on the maintenance dose after 56 weeks |
| Wegovy | Lost up to 15% of their starting weight on the maintenance dose after 68 weeks |
| Mounjaro | Lost up to 22.5% of their starting weight on the 15 mg maintenance dose after 72 weeks |
It is important to emphasize that weight loss medications are intended to be used adjunctively alongside a comprehensive weight management plan. This plan should include dietary modifications to create a calorie deficit and regular physical activity to promote healthy weight loss and improve overall health outcomes.
Potential Side Effects of Weight Loss Medications
Taking weight loss medications, whether in tablet or injection form, can sometimes lead to side effects. It’s important to be aware of these potential effects and discuss them with your doctor before starting treatment.
Specific side effects you may experience can vary depending on the type of medication you’re taking. However, some common side effects across various weight loss medications include:
- Gastrointestinal: Abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation
- Central nervous system: Headache, fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Taste changes
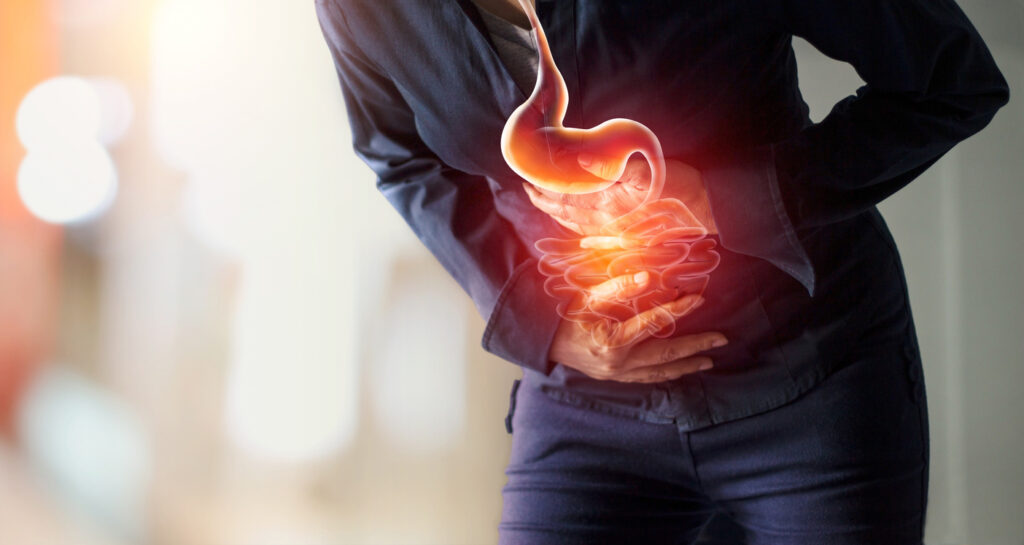

Other effects:
Rapid weight loss, even through medication, can have physical effects. These may include:
- Loose skin: As you lose weight, your skin may not have time to shrink completely, leading to sagging in some areas.
- Stretch marks: Rapid changes in skin size can cause stretch marks, which are reddish or purplish lines on the skin.
It is important to discuss these potential side effects with your healthcare professional before starting any weight loss medication. They can advise you on what to expect and how to manage any side effects that may occur.
In Summary:
Weight loss medications can be a valuable tool to aid weight loss and management, especially for those struggling to achieve their goals with lifestyle changes alone. However, their use should be carefully considered in consultation with a healthcare professional to ensure safety and effectiveness within a comprehensive weight management plan.
Key Takeways
- Not a Standalone Solution: Weight loss medications should not be viewed as a quick fix or a magic bullet. They are most effective when used in conjunction with a healthy diet and regular physical activity to create a sustainable weight management plan.
- Personalised Approach: A thorough medical assessment is necessary before starting any weight loss medication. This assessment allows a healthcare professional to identify the most appropriate medication for each patient, considering factors such as medical history and potential medication interaction.
- Potential Side Effects: All medications can have side effects, and weight loss medications are no exception. The specific side effects can vary depending on the medication. Discussing these potential side effects with your doctor is crucial to ensure they are manageable and do not outweigh the potential benefits.
- Long-Term Weight Management: Weight regain is a concern after stopping most weight loss medications. Developing and maintaining healthy lifestyle habits, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, are essential for long-term weight management success.
Ready to lose weight? Priman can help!
References
alli 60 mg hard capsules – Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) – (emc) (no date) Org.uk. Available at: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/6533/smpc.
Billes, S. K., Sinnayah, P. and Cowley, M. A. (2014) “Naltrexone/bupropion for obesity: An investigational combination pharmacotherapy for weight loss,” Pharmacological research: the official journal of the Italian Pharmacological Society, 84, pp. 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2014.04.004.
Examining Off-Label Prescribing of Ozempic for Weight-Loss (2023) Researchgate.net. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/371339511_Examining_Off-Label_Prescribing_of_Ozempic_for_Weight-Loss.
Gettman, L. (2023) “New drug: Tirzepatide (mounjaroTM),” The Senior care pharmacist, 38(2), pp. 50–62. doi: 10.4140/tcp.n.2023.50.
Government plans to tackle obesity in England (2023) Gov.uk. Available at: https://healthmedia.blog.gov.uk/2023/06/07/government-plans-to-tackle-obesity-in-england/.
Miles, K. E. and Kerr, J. L. (2018) “Semaglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus,” The Journal of pharmacy technology: jPT: official publication of the Association of Pharmacy Technicians, 34(6), pp. 281–289. doi: 10.1177/8755122518790925.
Mounjaro KwikPen 10mg solution for injection in pre-filled pen – Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) – (emc) (no date) Org.uk. Available at: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/15484/smpc.
Mysimba 8 mg/90 mg prolonged-release tablets – Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) – (emc) (no date) Org.uk. Available at: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/2684.
“Overview | Weight management: lifestyle services for overweight or obese adults | Guidance | NICE” (2014). Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ph5.
Rex, J. (2021) Orlistat. Morrisville, NC: Lulu.com.
Saxenda 6 mg/mL solution for injection in pre-filled pen – Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) – (emc) (no date) Org.uk. Available at: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/2313/smpc.
Semaglutide for managing overweight and obesity (2023) Org.uk. Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta875/resources/semaglutide-for-managing-overweight-and-obesity-pdf-82613674831813.
Singh, G., Krauthamer, M. and Bjalme-Evans, M. (2022) “Wegovy (semaglutide): A new weight loss drug for chronic weight management,” Journal of investigative medicine: the official publication of the American Federation for Clinical Research, 70(1), pp. 5–13. doi: 10.1136/jim-2021-001952.
Vanderheiden, A. et al. (2016) “Mechanisms of action of liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with high-dose insulin,” The journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism, 101(4), pp. 1798–1806. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-3906.
Wojtara, M. et al. (2023) “Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for chronic weight management,” Advances in medicine, 2023, pp. 1–7. doi: 10.1155/2023/9946924.
Xenical 120 mg hard capsules – Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) – (emc) (no date) Org.uk. Available at: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/2592.